Last week we talked about Building Envelope Code Compliance, the 2015 IRC and the performance path.
This week we are going to discuss the final compliance method, a new compliance method in the 2015 IRC, the Energy Rating Index.
Energy Rating Index, or ERI, is a calculated number, on a linear index scale, constructed with the ERI reference design having a value of 100 and a residential building that uses no net purchased energy having an index value of 0.
A one percent change in the total energy use of the rated design relative to the total energy use of the ERI reference design shall be represented by a change of 1 on the index scale. So, an ERI of 55 means that the proposed design outperforms the ERI reference design by 45%.
For the purpose of the Energy Rating Index, the code identifies that the ERI reference design shall meet the minimum requirements of the 2006 International Energy Conservation Code prescriptive requirements.
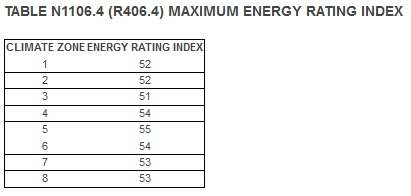
To qualify for ERI compliance, the maximum energy rating index, allowable by climate zone, is identified in table 1106.4:
For example, in Climate Zone 3, like Dallas, TX, to qualify for ERI compliance, the building would have an energy rating index of 51. This means that the building would use 49% less energy than the 2006 IECC code minimum for the same building.
Finally, a report that shows the proposed design meets the requirements of the Energy Rating Index is required using energy calculations from an energy modeling software tool, like:
-
REScheck™
-
COMcheck™
-
EnergyPro
-
Elite RHVAC
-
Wrightsoft Right-J8
-
Florida Solar Energy Center’s EnergyGauge